Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
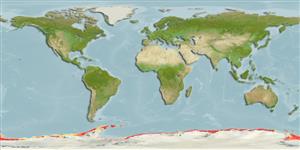
marin benthopélagique; profondeur 200 - 800 m (Ref. 5200). Polar; 60°S - 78°S, 180°W - 180°E (Ref. 5200)
Southern Ocean: Circum-Antarctic on Antarctic continental shelf. Northernmost records from vicinity of South Orkney Islands and Antarctic Peninsula.
Length at first maturity / Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm ?, range 23 - ? cm
Max length : 43.0 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 5200); common length : 30.0 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 2805)
Épines dorsales (Total) : 5 - 8; Rayons mous dorsaux (Total) : 38 - 42; Épines anales: 0; Rayons mous anaux: 32 - 36. Supraorbital ridge not crenulated. Middle lateral line restricted to caudal peduncle; lower lateral line originating from in front of anal-fin origin to above sixth anal ray. Maxilla extending to below anterior third of eye. Opercular bones with 2 upper and 3 lower spines. Preopercular-mandibular canal not joined to temporal canal. Pelvic fins extending beyond anal-fin origin. In life, pale grey, whitish ventrally. Differentiated by the dorsoventrally oval shape; the prominent distally rounded rostrum, pseudo-rostrum and pseudo-antirostrum; the clearly defined excisura ostii and pseudo-excisura ostii; the acutely constricted collum; and the well developed colliculli.
Ontogeny: The excisura ostii and the pseudo-excisura ostii become deeper and the crista inferior becomes less distinct with an increase in the fish size.
Common in shallower waters of the continental shelf, especially on banks less than 250 m deep in areas where local upwelling increase food supply (Ref. 6390). Postlarvae and pelagic juveniles are also found in the upper 100 m (Ref. 5200). Food consists of fishes and krill. Spawn in winter (Ref. 6390). Larval pelagic phase is long (Ref. 28915). Prey to penguins and seals (Ref. 6390). Utilized as a food fish (Ref. 5200).
Iwami, T. and K.-H. Kock, 1990. Channichthyidae. p. 381-389. In O. Gon and P.C. Heemstra (eds.) Fishes of the Southern Ocean. J.L.B. Smith Institute of Ichthyology, Grahamstown, South Africa. 462 p. (Ref. 5200)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435)
Menace pour l'homme
Harmless
Utilisations par l'homme
Pêcheries: intérêt commercial mineur
Outils
Articles particuliers
Télécharger en XML
Sources Internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): -1.8 - 1.4, mean -0.8 °C (based on 825 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 1.0000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00095 (0.00056 - 0.00163), b=3.54 (3.39 - 3.69), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species & (Sub)family-body (Ref.
93245).
Niveau trophique (Ref.
69278): 3.2 ±0.2 se; based on diet studies.
Résilience (Ref.
120179): Milieu, temps minimum de doublement de population : 1,4 à 4,4 années (Fec = 393-862).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low to moderate vulnerability (33 of 100).
Climate Vulnerability (Ref.
125649): High vulnerability (64 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 24.1 [13.1, 52.5] mg/100g; Iron = 0.394 [0.164, 0.807] mg/100g; Protein = 16.6 [14.9, 18.4] %; Omega3 = 0.238 [0.110, 0.509] g/100g; Selenium = 23 [8, 56] μg/100g; VitaminA = 20.2 [4.2, 101.6] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.466 [0.301, 0.712] mg/100g (wet weight);