Élasmobranches (requins et raies) (sharks and rays) >
Carcharhiniformes (Ground sharks) >
Atelomycteridae (Coloured catsharks)
Etymology: Atelomycterus: ateles (Gr.), imperfect, unfilled or exempt; mycteros (Gr.), nostril, referring to lack of posterior nasal valve. (See ETYFish); baliensis: -ensis, Latin suffix denoting place: Bali, Indonesia, only known area of occurrence. (See ETYFish).
More on authors: White, Last & Dharmadi.
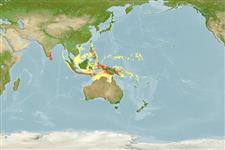
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
marin démersal. Tropical
Western Pacific: known only from the Indonesian island of Bali.
Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 47.4 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 54850)
Description synthétique
Clés d'identification | Morphologie | Morphométrie
A relatively small (max. size 474 mm TL) Atelomycterus with the following combination of characters: relatively short preoral length, 4.0-4.6% T; short interdorsal space, 11.6-12.9% TL; high pectoral-pelvic to pelvic-anal ratio 1.28-1.48; dorsal fins weakly falcate, with posterior margins vertical or sloping anteroventrally from fin apices; prebranchial denticles strongly tricuspid with narrow, elongate medial cusps; claspers of adults short, not stubby, not tapering sharply distally, outer length 8.3-9% TL, base width 5.4-6.3% of outer length; clasper glans covering more than half of clasper; cover rhipidion relatively narrow; rhipidion large, relatively low, and only partly concealed by cover rhipidion and exorhipidion; exorhipidion small with proximal end well behind distal end of cover rhipidion; total vertebral centra 154-163, precaudal centra 101-106; dorsal surface with well-defined dark saddles consisting mainly of four, partly coalesced, diffuse-edged, dark brown blotches; white partly coalesced, diffuse-edged, dark brown blotches; white spots absent from body and rarely on fins; inner margin of pale tips of dorsal fins orientated almost vertically; upper pectoral fin lacking a broad, sharply defined whitish margin.
Biology unknown; presumably reef-dwelling, inhabiting holes and crevices on reefs, like other related catsharks. Presumably oviparous. Diet probably dominated by small invertebrates . Caught irregularly by fisheries operating over coral reefs. Utilized for its meat but of limited value (Ref.58048).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturities | Reproduction | Spawnings | Egg(s) | Fecundities | Larves
White, W.T., P.R. Last and Dharmadi, 2005. Description of a new species of catshark, Atelomycterus baliensis (Carcharhiniformes: Scyliorhinidae) from eastern Indonesia. Cybium 29(1):33-40. (Ref. 54850)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435)
Menace pour l'homme
Harmless
Utilisations par l'homme
Outils
Articles particuliers
Télécharger en XML
Sources Internet
Estimates based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5156 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Niveau trophique (Ref.
69278): 3.7 ±0.3 se; based on size and trophs of closest relatives
Résilience (Ref.
120179): Faible, temps minimum de doublement de population : 4,5 à 14 années (Low fecundity (RF)).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Moderate vulnerability (37 of 100).