Teleostei (teleosts) >
Cyprinodontiformes (Rivulines, killifishes and live bearers) >
Fundulidae (Topminnows and killifishes)
Etymology: Fundulus: Latin, fundus = bottom; a peculiar name for a topminnow, coined for a bottom species of Atlantic coast being "the abode of the fundulus mudfish" (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Linnaeus.
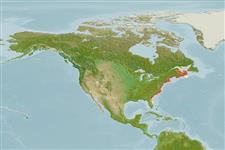
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Marine; freshwater; brackish; benthopelagic; non-migratory. Temperate; 10°C - 24°C (Ref. 12468); 52°N - 28°N, 82°W - 55°W
Western Atlantic: Gulf of St. Lawrence to northeast Florida, USA. Two subspecies were previously recognized: Fundulus heteroclitus heteroclitus and Fundulus heteroclitus macrolepidotus (Ref. 86798). Introduced to southern Portugal and southern Spain (Ref. 59043).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ?, range 4 - ? cm
Max length : 15.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 27139); common length : 8.9 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 12193); max. reported age: 4 years (Ref. 59043)
Distinguished from nearly identical species Fundulus grandis by having the following characters: more convex upper profile; dark bars alternating with silvery interspaces on side; small ocellus at rear of dorsal fin of male; and each mandible with 4 pores (Ref. 86798).
Facultative air-breathing (Ref. 126274); Occurs in saltwater marshes, tidal creeks and nearby fresh water (Ref. 86798). A resident intertidal species with homing behavior (Ref. 32612). Adults are mainly found in saltwater marshes and in tidal creeks. They may leave tide pools if aquatic conditions become inhospitable (Ref. 31184). They also enter fresh water to a limited extent (Ref. 7251). Not a seasonal killifish. They breathe air when out of water (Ref. 31184). Difficult to maintain in aquariums (Ref. 27139). Introduction has caused the decline of native species and near extinction of Aphanius baeticus in southwestern Spain (Ref. 59043).
Deposits eggs in the shells of Modiolus demissus (Ref. 26281).
Page, L.M. and B.M. Burr, 2011. A field guide to freshwater fishes of North America north of Mexico. Boston : Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 663p. (Ref. 86798)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquarium: commercial
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 6.1 - 23.7, mean 9.3 °C (based on 163 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00933 (0.00721 - 0.01209), b=3.17 (3.10 - 3.24), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.6 ±0.48 se; based on food items.
Generation time: 1.5 ( na - na) years. Estimated as median ln(3)/K based on 1
growth studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (tm<1; tmax=4).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low vulnerability (19 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 82.9 [39.2, 188.9] mg/100g; Iron = 0.442 [0.225, 0.881] mg/100g; Protein = 17.9 [16.5, 19.2] %; Omega3 = 0.594 [0.249, 1.464] g/100g; Selenium = 4.78 [1.73, 11.60] μg/100g; VitaminA = 29.2 [7.9, 115.4] μg/100g; Zinc = 1.09 [0.70, 1.68] mg/100g (wet weight);