Classification / Names
Common names | Synonyms | Catalog of Fishes(genus, species) | ITIS | CoL | WoRMS | Cloffa
Teleostei (teleosts) >
Clupeiformes (Herrings) >
Engraulidae (Anchovies) > Engraulinae
Etymology: Encrasicholina: Greek, egkrasicholos, -os, -on = mixed with spleen.
Eponymy: Charles Walter De Vis (1829–1915) was a zoologist and clergyman. [...] (Ref. 128868), visit book page.
More on author: Whitley.
Issue
formerly ENGR Stol 7
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Marine; brackish; reef-associated. Tropical; 32°N - 28°S, 43°E - 173°W (Ref. 189)
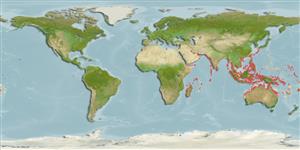
Indo-Pacific: widespread in the northern part of the Indian Ocean (Gulf of Aden, but apparently not the Red Sea nor Kenya, the Persian Gulf, India, Andaman Islands) and Western Central Pacific (Indonesia, Thailand, north to at least Taiwan Island, south to northern Australia; also eastward to Fiji and Tonga).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 6.1, range 4 - ? cm
Max length : 9.7 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 55634); 10.0 cm TL (female); max. published weight: 8.00 g (Ref. 55634); max. published weight: 8.00 g
Anal spines: 0; Anal soft rays: 18 - 20. Diagnosis: Body rather cylindrical, belly rounded, with 5-6, rarely 3 or 4, sharp needle-like pre-pelvic scutes; maxilla tip pointed, projecting beyond second supra-maxilla and reaching to sub-operculum; isthmus short, preceded by a small bony plate on urohyal between branchial membranes; lower gillrakers 20-27; unbranched dorsal and anal finrays 3, anal fin short, with usually 15-17 branched finrays; in life, a bright silver band on flank, with a thin blue line above, back blue/grey (Ref. 189). It closely resembles Encrasicholina heteroloba, which has only 2 unbranched dorsal and anal finrays, a dull silver/grey band on flank, and the back beige; Encrasicholina oligobranchus has only 17-18 gillrakers; other species of Encrasicholina have a fleshy urohyal plate and a maxilla tip blunt and not projecting beyond the second supra-maxilla; species of Stolephorus have a long isthmus reaching to the margin of the branchial membrane (Ref. 189).
Whitehead, P.J.P., G.J. Nelson and T. Wongratana, 1988. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 7. Clupeoid fishes of the world (Suborder Clupeoidei). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of the herrings, sardines, pilchards, sprats, shads, anchovies and wolf-herrings. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(7/2):305-579. Rome: FAO. (Ref. 189)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial; bait: usually
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 25.1 - 29.3, mean 28.5 °C (based on 3195 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5039 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00550 (0.00473 - 0.00639), b=3.12 (3.08 - 3.16), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.3 ±0.1 se; based on diet studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): High, minimum population doubling time less than 15 months (K=2.00-5.04; tm=0.29; tmax=1.7).
Prior r = 1.19, 95% CL = 0.79 - 1.79, Based on 1 data-limited stock assessment.
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low vulnerability (10 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 239 [65, 779] mg/100g; Iron = 1.47 [0.53, 3.85] mg/100g; Protein = 19.7 [17.2, 21.8] %; Omega3 = 0.207 [0.089, 0.481] g/100g; Selenium = 39.9 [12.9, 127.6] μg/100g; VitaminA = 37.5 [9.1, 191.7] μg/100g; Zinc = 2.21 [1.24, 5.33] mg/100g (wet weight); based on
nutrient studies.