Teleostei (teleosts) >
Clupeiformes (Herrings) >
Engraulidae (Anchovies) > Coiliinae
Etymology: Coilia: Greek, koilia, -as = abdomen, hollow (Ref. 45335).
Eponymy: Valenciennes did not explain who Reynald was. [...] (Ref. 128868), visit book page.
More on author: Valenciennes.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
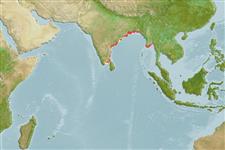
Marine; freshwater; brackish; pelagic-neritic; amphidromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 0 - 50 m (Ref. 189). Tropical; 26°N - 7°N, 76°E - 99°E (Ref. 189)
Indian Ocean: eastern coasts and estuaries of India, and also Irrawaddy River at Rangoon, Myanmar. All Indian references to a species with over 7 pectoral filaments must apply to Coilia reynaldi.
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 15.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 189)
Short description
Identification keys | Morphology | Morphometrics
Dorsal spines (total): 0; Anal spines: 0; Anal soft rays: 80. Body tapering, belly rounded before pelvic fins, with 6 to 9 + 7 to 11 = 13 to 19 keeled scutes from just behind pectoral fin base to anus. Maxilla short, not reaching to edge of gill cover. Pectoral fin with 10 to 13 long filaments; the branched fin rays much shorter those of pelvic fin.
Occurs in coastal and tidal stretches of rivers, but apparently no data on salinity tolerances. Its presence above Barrackpore on the Hooghly in India suggests that it can live in freshwater. Larvae feed on copepods; thereafter mainly on copepods, but also on prawns, larval decapods and other crustaceans. Breeds in the lower parts of estuaries. The time and duration of the breeding season reported vary for different estuaries in India.
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Breeds in lower parts of estuaries (Ref. 189). Spawn in school (Ref. 205).
Whitehead, P.J.P., G.J. Nelson and T. Wongratana, 1988. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 7. Clupeoid fishes of the world (Suborder Clupeoidei). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of the herrings, sardines, pilchards, sprats, shads, anchovies and wolf-herrings. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(7/2):305-579. Rome: FAO. (Ref. 189)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: minor commercial
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 27.9 - 28.9, mean 28.4 °C (based on 48 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5001 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00282 (0.00126 - 0.00632), b=3.10 (2.92 - 3.28), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this Genus-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.3 ±0.46 se; based on food items.
Generation time: 1.6 ( na - na) years. Estimated as median ln(3)/K based on 1
growth studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): High, minimum population doubling time less than 15 months (K=0.7).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low vulnerability (20 of 100).