Élasmobranches (requins et raies) (sharks and rays) >
Carcharhiniformes (Ground sharks) >
Carcharhinidae (Requiem sharks)
Etymology: Carcharhinus: karcharos (Gr.), sharp or jagged; rhinus, an ancient name for sharks, from rhine (Gr.), rasp, both words alluding to a shark's jagged, rasp-like skin. (See ETYFish); altimus: Latin for highest, allusion not explained nor evident. (See ETYFish).
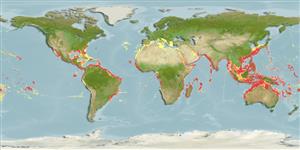
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
marin récifal; profondeur 12 - 810 m (Ref. 58302), usually 80 - 220 m (Ref. 9253). Subtropical; 46°N - 31°S, 180°W - 180°E
Circumglobal: tropical to temperate watersin the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans. Introduced in the Mediterranean via Gibralltar.
Length at first maturity / Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm 230.0, range 205 - 282 cm
Max length : 300 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 2334); common length : 250 cm TL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 26999); poids max. publié: 167.8 kg (Ref. 40637)
Épines dorsales (Total) : 0; Épines anales: 0. A heavily-bodied, cylindrical shark with a large, long and broad snout, long nasal flaps and high, triangular, saw-edged upper teeth; interdorsal ridge high and prominent; pectoral and dorsal fins large and straight (Ref. 5578). Grayish with no conspicuous markings, white below (Ref. 5578); inner corners of pectoral fins blackish (Ref. 9997).
Found near the edge of the continental and insular shelves and uppermost slopes (Ref. 244). Rare in shallow waters (Ref. 9997), bottom associated near shelf breaks and drop-offs; young may occur at 25 m (Ref. 58302). Feeds on bony fishes, other sharks, stingrays, and cuttlefish (Ref. 244). Viviparous (Ref. 50449). Utilized for fishmeal, liver oil, and shagreen (Ref. 9997). Minimum depth reported taken from Ref. 244.
Viviparous, placental (Ref. 50449). Gives birth every second year with 1-13 (average 9) pups per litter (Ref. 58048). In the Mediterranean, sharks give birth in August and September, however in Madagascar, young are born in September and October (Ref. 244). Size at birth 60-75 cm (Ref. 6871); 70-90 cm TL (Ref.58048). Distinct pairing with embrace (Ref. 205).
Compagno, L.J.V., 1984. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 4. Sharks of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date. Part 2 - Carcharhiniformes. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(4/2):251-655. Rome: FAO. (Ref. 244)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435)
Utilisations par l'homme
Pêcheries: intérêt commercial mineur
Outils
Articles particuliers
Télécharger en XML
Sources Internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 13.8 - 26.5, mean 19.9 °C (based on 875 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00331 (0.00178 - 0.00617), b=3.11 (2.96 - 3.26), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species & Genus-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Niveau trophique (Ref.
69278): 4.5 ±0.3 se; based on diet studies.
Résilience (Ref.
120179): Très faible, temps minimum de doublement de population supérieur à 14 ans (Fec=1-13;).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Very high vulnerability (90 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 2.96 [0.55, 15.71] mg/100g; Iron = 0.338 [0.086, 0.978] mg/100g; Protein = 22.9 [20.0, 25.1] %; Omega3 = 0.186 [0.069, 0.461] g/100g; Selenium = 24 [8, 71] μg/100g; VitaminA = 26.4 [9.0, 79.0] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.305 [0.149, 0.601] mg/100g (wet weight);