>
Scombriformes (Mackerels) >
Scombridae (Mackerels, tunas, bonitos) > Scombrinae
Etymology: Scomberomorus: Latin, scomber = mackerel + Greek, moros = silly, stupid (Ref. 45335).
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Écologie
marin; saumâtre; océanodrome (Ref. 51243); profondeur 1 - 100 m (Ref. 6390), usually ? - 30 m (Ref. 6390). Tropical; 7°S - 35°S, 110°E - 157°E (Ref. 168)
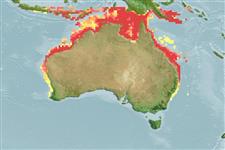
Western Pacific: largely confined to inshore coastal waters of southern Papua New Guinea and northern and eastern Australia, from Shark Bay and Onslow, Western Australia to Sydney, New South Wales. This species was confused with Scomberomorus guttatus.
Length at first maturity / Taille / Poids / Âge
Maturity: Lm ?, range 48 - ? cm
Max length : 100.0 cm FL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 168); common length : 80.0 cm FL mâle / non sexé; (Ref. 168); poids max. publié: 12.2 kg (Ref. 3132)
Épines dorsales (Total) : 16 - 18; Rayons mous dorsaux (Total) : 17 - 19; Épines anales: 0; Rayons mous anaux: 16 - 20; Vertèbres: 48 - 49. Interpelvic process small and bifid. Lateral line gradually curving down toward caudal peduncle. Intestine with 2 folds and 3 limbs. Swim bladder absent. Body covered with small scales. Membrane of first dorsal fin jet black with large contrasting areas of intense white between the 6th and the last spine. Sides of adults marked with about three indefinite rows of indistinct bronze-gray blotches (absent in 9.5 cm juveniles).
Schooling species which moves into inshore waters, bays and estuaries of Queensland during the southern midwinter and early spring. Often inhabit very turbid coastal waters shallower than 30 m (Ref. 6390). Common length 50 to 80 cm FL (Ref. 12241). Seasonally migratory in the Gulf of Carpentaria and form mixed schools with S. commerson over shallow reefs offshore of Queensland. Trolling lines with lures such as metal spoons and cut bait are used by recreational and commercial fishermen. Mostly marketed fresh (Ref. 9987).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturities | Reproduction | Spawnings | Egg(s) | Fecundities | Larves
Collette, B.B. and C.E. Nauen, 1983. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 2. Scombrids of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of tunas, mackerels, bonitos and related species known to date. Rome: FAO. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(2):137 p. (Ref. 168)
Statut dans la liste rouge de l'IUCN (Ref. 130435)
Menace pour l'homme
Reports of ciguatera poisoning (Ref. 6390)
Utilisations par l'homme
Pêcheries: commercial; pêche sportive: oui
Outils
Articles particuliers
Télécharger en XML
Sources Internet
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 24.5 - 28.6, mean 27.4 °C (based on 302 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00832 (0.00383 - 0.01808), b=3.03 (2.86 - 3.20), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this Genus-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Niveau trophique (Ref.
69278): 4.5 ±0.8 se; based on diet studies.
Résilience (Ref.
120179): Milieu, temps minimum de doublement de population : 1,4 à 4,4 années (tm=1-2).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low to moderate vulnerability (33 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 38.2 [17.5, 147.4] mg/100g; Iron = 0.94 [0.43, 2.31] mg/100g; Protein = 21 [20, 22] %; Omega3 = 0.295 [0.178, 0.499] g/100g; Selenium = 66.7 [23.7, 308.3] μg/100g; VitaminA = 14.9 [2.9, 71.4] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.756 [0.504, 1.192] mg/100g (wet weight);