Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays) >
Orectolobiformes (Carpet sharks) >
Rhincodontidae (Whale shark)
Etymology: Rhincodon: rhinc, presumably a typographical error for rhine (Gr.), rasp, but often mistranslated as rhynchos (Gr.), snout; odon, tooth, referring to small, slightly curved teeth, “placed in longitudinal rows, and altogether so disposed towards the anterior edges of jaws as to exhibit the resemblance of a rasp or file lying across each” (See ETYFish); typus: Serving as type species of the genus (See ETYFish).
Eponymy: Camrin D Braun is an American ichthyologist. [...] (Ref. 128868), visit book page.
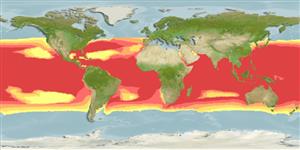
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Marine; pelagic-oceanic; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 0 - 1928 m (Ref. 106604), usually 0 - 100 m (Ref. 89972). Subtropical; 18°C - 30°C (Ref. 35465); 45°N - 48°S, 180°W - 180°E
Circumglobal, all tropical and warm temperate seas except the Mediterranean.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 500.0, range 440 - 560 cm
Max length : 1,700 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 48722); 2,000.0 cm TL (female); common length : 1,000 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 12757); max. published weight: 34.0 t (Ref. 48722); max. reported age: 80 years (Ref. 116781)
Dorsal spines (total): 0; Anal spines: 0. A huge, filter-feeding, blunt-headed shark with a distinct checkerboard pattern of yellow or white spots, on grey, bluish or blue-grey to green-brown back, white or yellowish underside, with horizontal and vertical stripes on back and sides of body; head broad and flat; snout short; mouth almost terminal, huge and transverse in front of eyes; prominent ridges on body, lowest terminating in a keel on caudal peduncle (Ref. 58085, 114967); nostrils with rudimentary barbels; long nasoral grooves; spiracles close to and larger than eyes; 5 exceptionally large gill openings, the fifth behind pectoral fin (Ref. 110893, 114967); numerous small, scale-like teeth and feeds by filtering plankton with special sieve-like modifications of the gill bars (Ref. 26938).
World's largest fish, but is harmless to humans (Ref. 6871). Grows up to 20m (Ref. 48722). Often seen offshore but coming close inshore, sometimes entering lagoons or coral atolls (Ref. 247). Sometimes seen cruising near outer wall (Ref. 26938). Reported to frequent shallow water areas near estuaries and river mouths, sometimes during seasonal shrimp blooms (Ref. 48696). Found singly, or in aggregations of over 100 individuals (Ref. 5578). Often associated with groups of pelagic fishes, especially scombrids (Ref. 247). Highly migratory between ocean basins and national jurisdictions, but returns to the same sites annually (Ref. 48672). Feed on planktonic and nektonic prey, such as small fishes (sardines, anchovies, mackerel, juvenile tunas and albacore), small crustaceans and squids (Ref. 247). Often seen in a vertical position with the head at or near the surface when feeding (Ref. 13571). When actively feeding on zooplankton the sharks turn their heads from side to side, with part of the head lifted out of the water, and the mouth opened and closed 7-28 times per minute; these suction gulps were synchronized with the opening and closing of the gill slits (Ref. 35680). Ovoviviparous, with litter size of over 300 pups (Ref. 37816, 43278). Females of 438 to 562 cm are immature (FIGIS 09/2003). Utilized fresh, frozen, dried and salted for human consumption, liver processed for oil, fins used for shark-fin soup, offal probably for fishmeal (Ref. 13571), cartilage for health supplements and skin for leather products (Ref. 48723). Used in Chinese medicine (Ref. 12166). Highly valued commodity in ecotourism operations. Populations have been depleted in several countries by harpoon fisheries (Ref. 48696). Estimated longevity of 80.4 yrs is much larger than reported maximum age 38 yrs based on vertebral bands for a female of 11.9 m TL. Maximum length of up to 21 m and weight of up to 42 tons have been reported (Ref. 116781), but probably the most reliably measured size so far is 12 m TL (Ref. 26319).
Distinct pairing with embrace (Ref. 205). Ovoviviparous (Ref. 35465). Embryos feed solely on yolk (Ref. 50449). Late term embryos shed their egg case within the uterus at a size of 58 to 64 cm TL (ovovivipary). The smallest free-living species are from 55-56 cm long, the smallest of which had an umbilical scar. A pregnant female has recently been found with 300 embryos, the largest of which were 58-64 cm (Refs. 26346, 35678).
Colman, J.G., 1997. A review of the biology and ecology of the whale shark. J. Fish Biol. 51(6):1219-1234. (Ref. 26319)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 19.6 - 29, mean 27.3 °C (based on 5510 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 1.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00389 (0.00180 - 0.00842), b=3.12 (2.94 - 3.30), in cm total length, based on all LWR estimates for this body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.6 ±0.5 se; based on diet studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Very Low, minimum population doubling time more than 14 years (K=0.02; Fec=16-300).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Very high vulnerability (87 of 100).