Teleostei (teleosts) >
Eupercaria/misc (Various families in series Eupercaria) >
Haemulidae (Grunts) > Plectorhinchinae
Etymology: Plectorhinchus: Greek, plektos = plaited + Greek, rhyngchos = snout (Ref. 45335); caeruleonothus: Name from the Latin words 'caeruleo' for blue and 'nothus' for bastard when combined as ‘Blue Bastard’ which has been commonly applied to this species by anglers for many years; referring to its blue sheen in life and difficulty to hook and land on artificial fly.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Marine; reef-associated; depth range 6 - 30 m (Ref. 103290). Tropical; 9°S - 25°S, 101°E - 147°E (Ref. 103290)
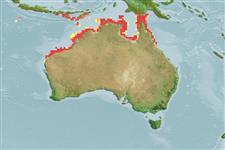
Distribution
Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Point map | Introductions | Faunafri
Southwest Pacific: Australia (Western Australia toi Queensland).
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 100.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 103290)
Short description
Identification keys | Morphology | Morphometrics
Dorsal spines (total): 12; Dorsal soft rays (total): 18 - 20; Anal spines: 3; Anal soft rays: 6 - 7. This species is distinguished by the following features: D XII, 18-20 (rarely 20); A III, 6-7 (rarely III, 6); pectoral-fin rays 16-17 (usually 17); lateral-line scales 56-61 (modally 59); transverse scale rows above lateral line 15; gill rakers 7-9 + 18-20 = 25-29 (modally 26); in juveniles, pelvic fins reaching anus, slightly short of anus in adults; nostrils minute, 0.4-0.8 % SL, 2-3 times in distance from posterior nostril to eye; when fresh colouration in adults with body uniformly silver-grey, cheek and opercles blue-grey, rim of orbit and dorsal edge of maxilla dusky yellow, posterior margin of opercular membrane silver-grey, non-contrasting with remainder of opercle and adjacent body (Ref. 103290).
This species is found on sand, rubble and reef bottom but mostly in the intertidal zone, or shallow reef; one specimen trawled in a depth of 30 m. The most southerly record is a large individual estimated to be 100 cm in total length. Large individuals are most often solitary, foraging diurnally over relatively open expanses of soft substrate. Agonistic behavioural interactions have been recorded between individuals, individuals have often been observed to interact highly aggressively, engaging in one-on-one conflicts (Ref. 103290).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Johnson, J.W. and J.W. Wilmer, 2015. Plectorhinchus caeruleonothus, a new species of sweetlips (Perciformes: Haemulidae) from northern Australia and the resurrection of P. unicolor (Macleay, 1883), a species previously confused with P. schotaf (Forsskål, 1775). Zootaxa 3985(4):491-522. (Ref. 103290)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: bycatch
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01413 (0.00689 - 0.02895), b=3.00 (2.83 - 3.17), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this Genus-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 3.9 ±0.6 se; based on size and trophs of closest relatives
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Very Low, minimum population doubling time more than 14 years (Preliminary K or Fecundity.).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): High vulnerability (60 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 21.8 [8.7, 40.3] mg/100g; Iron = 0.445 [0.233, 0.856] mg/100g; Protein = 19.4 [17.5, 21.3] %; Omega3 = 0.106 [0.058, 0.178] g/100g; Selenium = 36.5 [20.4, 62.3] μg/100g; VitaminA = 57.3 [21.5, 147.8] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.964 [0.681, 1.396] mg/100g (wet weight);