Teleostei (teleosts) >
Lophiiformes (Anglerfishes) >
Antennariidae (Frogfishes)
Etymology: Antennarius: From Latin, antenna, antemna = sensory organ (Ref. 45335).
More on author: Shaw.
Issue
Chinese common names from Ref. 31517 should correspond to the different species names seen in the book.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
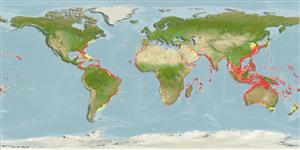
Marine; brackish; reef-associated; depth range 10 - 219 m (Ref. 9710), usually ? - 40 m (Ref. 5288). Subtropical; 43°N - 50°S, 88°W - 154°W (Ref. 57378)
Eastern Atlantic: off the African coast, from Senegal to Southwest Africa, with a single record from St. Helena. Western Atlantic: off the coast of New Jersey (USA), Bermuda, Bahamas, Gulf of Mexico and throughout the island groups of the Caribbean to the southernmost coast of Brazil. Indo-Pacific: Red Sea and the East African coast to the Society and Hawaiian islands, north to Japan, south to Australia and New Zealand.
Not in Eastern Pacific (Ref. 123477 ver. 09Nov2021).
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 25.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 48635); common length : 10.0 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 3585); max. published weight: 32.90 g (Ref. 118626)
Dorsal spines (total): 3; Dorsal soft rays (total): 11 - 12; Anal spines: 0; Anal soft rays: 7. Diagnosis: body short and globose; mouth large with many small, villiform teeth; skin rough, covered with bifurcate dermal spinules; pectoral-fin lobes attached to sides of body; illicium at most as long as second dorsal-fin spine; head, body and fins entirely covered with rough, parallel, dark streaks (Ref. 57225).
Inhabit rocky and coral reefs, on rocks, sand or rubble (Ref. 9710). Found in weedy estuaries along the east coast of southern Africa (Ref. 4113). Occurring in marine or brackish waters (Ref. 57225). In the Atlantic, it is found at an average depth of 40 m (Ref. 5288). Benthic (Ref. 58302). Observed to inflate itself greatly like the puffers (Ref. 5521). Oviparous. Males have more intense coloration and extended cutaneous appendages than females (Ref. 205). Eggs are bound in ribbon-like sheath or mass of gelatinous mucus called 'egg raft' or 'veil' (Ref. 6773).
Life cycle and mating behavior
Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Oviparous. Males have more intense coloration and extended cutaneous appendages than females (Ref. 205). Eggs are bound in ribbon-like sheath or mass of gelatinous mucus called 'egg raft' or 'veil' (Ref. 6773).
Pietsch, T.W. and D.B. Grobecker, 1987. Frogfishes of the world. Systematics, zoogeography, and behavioral ecology. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. 420 p. (Ref. 6773)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: of no interest; aquarium: commercial
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 18.2 - 28.6, mean 27 °C (based on 287 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5005 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.02630 (0.01029 - 0.06725), b=2.96 (2.73 - 3.19), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this (Sub)family-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 4.2 ±0.7 se; based on diet studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): High, minimum population doubling time less than 15 months (Fec = 73,000).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low vulnerability (15 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 26.8 [11.8, 72.2] mg/100g; Iron = 0.576 [0.292, 1.139] mg/100g; Protein = 19.7 [17.1, 23.0] %; Omega3 = 0.214 [0.076, 0.560] g/100g; Selenium = 15.7 [6.2, 38.7] μg/100g; VitaminA = 88.5 [18.8, 404.0] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.736 [0.437, 1.191] mg/100g (wet weight);