Teleostei (teleosts) >
Cichliformes (Cichlids, convict blennies) >
Cichlidae (Cichlids) > Pseudocrenilabrinae
Etymology: Oreochromis: Latin, aurum = gold + Greek, chromis = a fish, perhaps a perch (Ref. 45335); karomo: Karomo is the local name of the species (Ref. 2).
More on author: Poll.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
Freshwater; benthopelagic. Tropical; 22°C - 28°C (Ref. 2060); 4°S - 6°S
Africa: endemic to Malagarasi River basin, Tanzania (Ref. 2, 118630, 118638).
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 28.0 cm SL male/unsexed; (Ref. 4967)
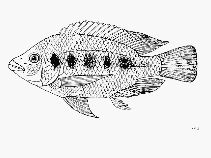
Dorsal spines (total): 15 - 16; Dorsal soft rays (total): 12 - 13; Anal spines: 3; Anal soft rays: 10 - 11; Vertebrae: 29. Diagnosis: A large bodied Oreochromis, characterised by elongated jaws, projecting forwards to form a long snout, with the tooth-bands meeting in the horizontal plane; broad bands of tricuspid teeth, with long, slender shafts and curved crowns, arranged in broad bands; maxilla with a flange resting on the premaxilla at the curve between its two arms; and dorsal region and flanks dark green/olive, ventral region lighter (Ref. 2, 118638). A tasseled species (Ref. 2). Fins of ripening males dark with orange lappets on the dorsal, female fins plain grey/olive (Ref. 118638). Females and non-breeding males have 3 large blotches on the flanks (Ref. 118638). Fully ripe males are purplish blue with dark spots on the flank scales, a blue-green head, bright blue lips and have blue-white stripes and spots on the dorsal, anal and tail fins; the dorsal and tailfins have broad orange margins, and there is a long, branched orange/red genital tassel (Ref. 118638).
Body shape (shape guide): short and / or deep.
Males were seen scooping up algal debris from the bottom, and occasionally they moved to the adjacent weed beds and rasp epiphytic algae (Ref. 2). A maternal mouthbrooder (Ref. 2, 118638); males defend territories in shallow water, building a small platform of fine sand in the centre of a small pit (Ref. 118638). Important in swamp fishery (Ref. 4967), and an important component of the fisheries catch in Lakes Sagera and Nyamagoma; potential as an aquaculture species (Ref. 118638). The IUCN status is critically endangered, based on small range, fishing pressure and habitat degradation (Ref. 118638). Excellent to eat; occurs in shallow water; common but localized (Ref. 53528).
A maternal mouthbrooder (Ref. 2, 118638); males defend territories in shallow water, building a small platform of fine sand in the centre of a small pit (Ref. 118638). Males construct and maintain a mating platform which is a circular area of fine sand (Ref. 2), usually only about 10-15cm in diameter which is much smaller than the length of the fish (Ref. 55077), surrounded by a low ridge, on the top of a mound about 10 cm high (Ref. 2), but the mound might be 1m in diameter at its base and 30cm high (Ref. 55074, 55077). The plaque of sand is kept very clean, making the nest visible from a considerable distance (Ref. 55077). Little boundary fighting between close neighbours, but males seen to drive away individuals of other species (e.g. Labeo and Clarias as well as other cichlids)(Ref. 2, 55077). Females are seen in the nests at various times throughout the day; the number of times a male spawns appears to be limited by the number of ripe females available; females cruise over the spawning grounds singly or in small shoals (Ref. 55077). Courtship behaviour short and not particularly complex (Ref. 364), including displaying by the male to attract a female, snout shaking (nose wagging) and tassel dragging (Ref. 364, 55077). Female lays a batch of eggs and immediately picks them up while the male drags his tassel over the nest (Ref. 2, 55077), but it remains unclear whether the eggs are fertilised in the water or in the mouth of the female (Ref. 55077). Two, 3 or more batches of eggs may be laid by the same female before she leaves the nest (Ref. 2, 55077), and the larger the female the more numerous the eggs (Ref. 55077). Normal spawning generally takes less than 5 minutes (Ref. 55077). Breeding individuals spend little time feeding (Ref. 2), and males do not leave their territory to feed (Ref. 5507). Young of 11 mm still with large yolk sacs were the largest seen from the mouth of a female (Ref. 55077). Young of 2-6cm remain in schools in the shallows (Ref. 2, 55077).
Trewavas, E., 1983. Tilapiine fishes of the genera Sarotherodon, Oreochromis and Danakilia. British Mus. Nat. Hist., London, UK. 583 p. (Ref. 2)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2025-2)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: commercial; aquaculture: likely future use; aquarium: commercial
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01862 (0.00830 - 0.04177), b=3.01 (2.82 - 3.20), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this (Sub)family-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 2.0 ±0.00 se; based on food items.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (Fec=250).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low vulnerability (24 of 100).
🛈