Scyliorhinus canicula (Linnaeus, 1758)
Lesser spotted dogfish
個人による観察記録の追加 Fish Watcher
| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |
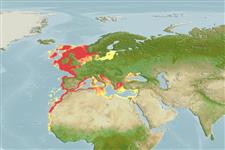
|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Scyliorhinus canicula AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
Upload your 写真 and ビデオ
Pictures | グーグルの画像Scyliorhinus canicula
Picture by Aquarium Kiel
Pictures | グーグルの画像Scyliorhinus canicula
Picture by Aquarium Kiel
Netherlands country information
Common names:
Gevlekte hondshaai, Hondshaai, Zeehond
Occurrence: native
Salinity: marine
Abundance: common (usually seen) | Ref: Nijssen, H. and S.J. de Groot, 1974
Importance: | Ref:
Aquaculture: | Ref:
Regulations: | Ref:
Uses: no uses
Comments: Known from the North Sea (Ref. 120402). In range Ref. 244.
National Checklist:
Country Information: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/resources/the-world-factbook/geos/nl.html
National Fisheries Authority:
Occurrences: Occurrences Point map
Main Ref: Nijssen, H. and S.J. de Groot, 1974
National Database:
Occurrence: native
Salinity: marine
Abundance: common (usually seen) | Ref: Nijssen, H. and S.J. de Groot, 1974
Importance: | Ref:
Aquaculture: | Ref:
Regulations: | Ref:
Uses: no uses
Comments: Known from the North Sea (Ref. 120402). In range Ref. 244.
National Checklist:
Country Information: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/resources/the-world-factbook/geos/nl.html
National Fisheries Authority:
Occurrences: Occurrences Point map
Main Ref: Nijssen, H. and S.J. de Groot, 1974
National Database:
Common names from other countries
分類 / Names 共通名の | 類義語 | Catalog of Fishes(部類, 種) | ITIS | CoL | WoRMS | Cloffa
板鰓亜鋼(サメとエイ類) (sharks and rays) > Carcharhiniformes (Ground sharks) > Scyliorhinidae (Cat sharks) > Scyliorhininae
Etymology: Scyliorhinus: skylion, Greek for dogfish or small shark; rhinus, from rhine (Gr.), rasp, alluding to a shark’s jagged, rasp-like skin (See ETYFish); canicula: Diminutive of canis (L.), dog; sharks were known as “sea dogs” and “dog-fishe” among mariners until the late 16th century, because of their ferocious pack-like feeding behavior (See ETYFish).
More on author: Linnaeus.
Etymology: Scyliorhinus: skylion, Greek for dogfish or small shark; rhinus, from rhine (Gr.), rasp, alluding to a shark’s jagged, rasp-like skin (See ETYFish); canicula: Diminutive of canis (L.), dog; sharks were known as “sea dogs” and “dog-fishe” among mariners until the late 16th century, because of their ferocious pack-like feeding behavior (See ETYFish).
More on author: Linnaeus.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range 生態学
海 底生の; 深さの範囲 10 - 780 m (Ref. 56504), usually 80 - 100 m (Ref. 81056). Subtropical; 63°N - 3°N, 32°W - 37°E
分布 国々 | 国連食糧農業機関の区域 | エコシステム | 事件 | Point map | 導入 | Faunafri
North Sea (sw coast of Sweden to Copenhagen, Denmark), Northeastern Atlantic Ocean (Ireland, United Kingdom, France, Portugal); Mediterranean Sea (Spain, France, Italy, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco); nw Africa, close to the Strait of Gibraltar and to the north of Mauritania (20º30’N); including Norwegian Sea.
Length at first maturity / サイズ / 重さ / 年齢
Maturity: Lm 50.0, range 35 - 64 cm
Max length : 100.0 cm TL オス/雌雄の選別がない; (Ref. 244); common length : 60.0 cm TL オス/雌雄の選別がない; (Ref. 4645); 最大公表体重: 3.7 kg (Ref. 128278); 最大記録サイズ: 12 年 (Ref. 81067)
Max length : 100.0 cm TL オス/雌雄の選別がない; (Ref. 244); common length : 60.0 cm TL オス/雌雄の選別がない; (Ref. 4645); 最大公表体重: 3.7 kg (Ref. 128278); 最大記録サイズ: 12 年 (Ref. 81067)
簡単な記述 検索表 | 形態学 | 形態計測学
This species is distinguished from all its congeners by the following characters: shallow nasoral grooves and laterally situated posterior nasal flaps (vs. no grooves and posterior flaps on the posterior border of the excurrent apertures in congeners, except in S. duhamelii); distance between the anterior nasal flaps 6-7.5 times smaller than the anterior nasal flap width (vs. 3.5-5 times smaller in S. duhamelii; two times in the other species); lower labial furrow 2.1-2.2 times smaller than mouth width (vs. more than 3 times in other species, except S. duhamelii). Colouration: color pattern with dark spots well-defined, predominantly smaller than spiracles (vs. no dark spots in S. capensis, S. comoroensis, S. hesperius, S. meadi, S. torazame, S. torrei; reticulated pattern in S. rotifer; dark spots predominantly larger than spiracles in S. cervigoni, S. garmani, S. haeckelii, S. stellaris; diffuse spots in S. duhamelii); clasper with rough terminal dermal cover (also found only in S. capensis) (Ref. 120402).
Most common catshark in coastal waters of Europe (Ref. 32804). Inhabits continental shelves and uppermost slopes. Found on sandy, coralline, algal, gravel or muddy bottoms. Occurs mainly between 10-100 m depth in the northeast Atlantic and up to 400 m depth in the Mediterranean Sea (Ref. 88187) and from 288-780 m in the eastern Ionian Sea (Ref. 56504). They sometimes occur in midwater. Nocturnal species, males resting on substrate and females hiding in shallow (0.5-1.5 m depth) caves and crevices during the day (Ref. 88835). Feed on a variety of benthic invertebrates, including mollusks, crustaceans, small cephalopods, polychaete worms, and small bony fishes (Ref. 244, 11889). Males have been found to forage in shallow prey-rich areas with soft sediment or areas covered with filamentous algae (Ref. 88836). Oviparous, with a single egg laid per oviduct at a time. Detect weak electric fields generated by other organisms (e.g. potential prey) (Ref. 10311). Utilized fresh and dried-salted for human consumption, also for oil and fishmeal.
Life cycle and mating behavior 成熟 | 繁殖 | 放精 | 卵 | 生産力 | 幼生
Oviparous, laying paired eggs (one per oviduct) in shallow subtidal areas, although some egg cases have been found in the deeper part of intertidal zones (Ref. 244). Embryos feed solely on yolk (Ref. 50449). The egg cases are anchored to macroalgae, sea grass or sessile erect invertebrates such as poriferans, bryozoans and hydroids (Ref. 32804, 58137). The capsules have tendrils at each corner used for anchorage purposes. Egg capsule size varies according to locality and female size (Ref. 244) and ranges between 4.9-7.0 cm length and 1.5-3.0 cm width (Ref. 88837). Egg cases may be deposited throughout the year, peaking in June and July (Ref. 32804). Recent studies estimate fecundity of females from the northeast Atlantic to be at around 29-62 pups (Ref. 32804). Fully formed pups hatch after 5-11 months, depending on water temperature (Ref. 244, 32804). Newly hatched pups are about 8-10 cm in length (Ref. 78469).
主な参考文献
Upload your references | 参考文献 | コーディネーター : Compagno, Leonard J.V. | 協力者
Soares, K.D.A. and M.R. De Carvalho, 2019. The catshark genus Scyliorhinus (Chondrichthyes: Carcharhiniformes: Scyliorhinidae): taxonomy, morphology and distribution. Zootaxa 4601(1):1-147. (Ref. 120402)
人間に対する脅威
Harmless
Human uses
水産業: 少数商業の; ゲームフィッシュ: はい
FAO(水産業: 代謝; publication : search) | FishSource | 私達の周りの海
より多くの情報
Population dynamics
成長のパラメーター
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
体長組成
Mass conversion
補充
豊度
成長のパラメーター
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
体長組成
Mass conversion
補充
豊度
用具
Bio-Quiz | E-book | 野外観察図鑑 | 検索表 | Length-frequency wizard | 生活史の基盤ツール | 目的のマップ | Classification Tree
| Catch-MSY |
特記事項
XMLをダウンロードして下さい
インターネットの情報源
Aquatic Commons | BHL | Cloffa | BOLDSystems | Websites from users | Check FishWatcher | CISTI | Catalog of Fishes(部類, 種) | DiscoverLife | DORIS | ECOTOX | Faunafri | Fishtrace | GenBank(ゲノム, ヌクレオチド) | GloBI | GOBASE | | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | IGFA World Record | MitoFish | 国のデーターベース | Otolith Atlas of Taiwan Fishes | 公共の水族館 | PubMed | Reef Life Survey | Scirus | SeaLifeBase | 生命の木 | Wikipedia(行く, 検索する) | World Records Freshwater Fishing | 動物に関する記録
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref. 115969): 7.2 - 16.2, mean 10.1 (based on 28 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref. 82804): PD50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00148 (0.00126 - 0.00174), b=3.20 (3.15 - 3.25), in cm Total Length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref. 93245).
栄養段階 (Ref. 69278): 3.8 ±0.3 se; based on diet studies.
回復力 (Ref. 120179): 低い, 4.5年~14年の倍増期間の最小個体群 (K=0.20; tm=9; Fec=96).
Prior r = 0.35, 95% CL = 0.23 - 0.53, Based on 1 full stock assessment.
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref. 59153): High vulnerability (59 of 100).
Climate Vulnerability (Ref. 125649): Moderate to high vulnerability (53 of 100).




