分類 / Names
共通名の | 類義語 | Catalog of Fishes(部類, 種) | ITIS | CoL | WoRMS | Cloffa
>
Gobiiformes (Gobies) >
Gobiidae (Gobies) > Gobiinae
Etymology: Trimma: Greek, trimma, -atos = something crushed (Ref. 45335); meristum: Name from the Greek ‘meristos’, meaning divided; referring to the two dichotomous branches in the fifth pelvic-fin ray resulting in four terminal tips, distinct feature of this new species.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / 深さの範囲 / distribution range
生態学
海 関連する礁; 深さの範囲 0 - 7 m (Ref. 100726). Tropical; 1°S - 21°S, 14°E - 180°E (Ref. 100726)
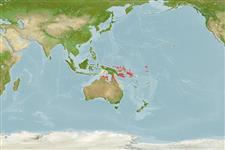
Western Pacific: Australia (Great Barrier Reef), Papua New Guinea (Bismark Archipelago) and Fiji.
サイズ / 重さ / 年齢
成熟: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 2.0 cm SL オス/雌雄の選別がない; (Ref. 119492)
簡単な記述
検索表 | 形態学 | 形態計測学
背面の脊椎 (合計) : 7; 背鰭 (合計) : 8; 肛門の骨: 1; 臀鰭: 7. This species is distinguished by the following characters: concave bony interorbital is less than half pupil-diameter in width; with a slight or no groove posterodorsal to the eye; scales in the midline of the predorsal 8-10; anal-fin rays 7; the fifth pelvic ray is branched twice dichotomously and subequal to the fourth in length, with a full basal membrane; the epaxial musculature reaches anteromedially to a point in line with the posterior margin of the pupil in adults; scale pockets on the head and body are strongly outlined by brown chromatophores (Ref. 100726).
Body shape (shape guide): fusiform / normal; Cross section: oval.
Species collected from jetty pilings, log debris, and concrete stairs at the water’s edge, at about 1-4 meters. It apparently have an affinity for sponge-encrusted surfaces, but the general area where it is observed is characterized by extensive silty mud substrata inhabited by a large number of burrowing gobies. It was not previously observed despite nearly 100 hours of scuba-diving because the collection site is immediately adjacent to shore at a busy shipyard where diving is usually banned during daylight hours. Most of the specimens were found on the inner side of a single pillar of the jetty, which was situated in total shade (Ref. 119492).
Life cycle and mating behavior
成熟 | 繁殖 | 放精 | 卵 | 生産力 | 幼生
Winterbottom, R. and D.F. Hoese, 2015. A revision of the Australian species of Trimma (Actinopterygii, Gobiidae), with descriptions of six new species and redescriptions of twenty-three valid species. Zootaxa 3934(1):001-102. (Ref. 100726)
IUCNのレッドリストの状況は (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Human uses
水産業: 興味がない
用具
特記事項
XMLをダウンロードして下さい
インターネットの情報源
Estimates based on models
Phylogenetic diversity index (参照
82804): PD
50 = 0.5000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01023 (0.00477 - 0.02194), b=3.01 (2.83 - 3.19), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this (Sub)family-body shape (Ref.
93245).
回復力 (参照
120179): 高い, 15か月以下の倍増期間の最小個体群 (Preliminary K or Fecundity.).
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Low vulnerability (10 of 100).
🛈