Etmopterus benchleyi Vásquez, Ebert & Long, 2015
Ninja lanternshark| Native range | All suitable habitat | Point map | Year 2050 |

|
| This map was computer-generated and has not yet been reviewed. |
| Etmopterus benchleyi AquaMaps Data sources: GBIF OBIS |
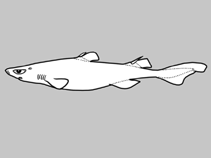
Google imageNo image available for this species;
drawing shows typical species in Etmopteridae.
Classification / Names Common names | Synonyms | Catalog of Fishes(genus, species) | ITIS | CoL | WoRMS | Cloffa
Etymology: Etmopterus: Greek, ethmos, -ou = sieve or ethmoides bone + Greek, pteron = wing, fin (Ref. 45335); benchleyi: Named for Peter Benchley, author of the movie Jaws and subsequently an avid shark conservationist.
Eponymy: Peter Benchley (1940–2006) was an American author and screenwriter, best known for writing Jaws (1974). [...] (Ref. 128868), visit book page.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range Ecology
Distribution Territories | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Point map | Introductions | Faunafri
Size / Weight / Age
Max length : 32.5 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 106129); 51.5 cm TL (female)
Short description Identification keys | Morphology | Morphometrics
Body shape (shape guide): elongated; Cross section: angular.
Life cycle and mating behavior Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Main reference
Upload your references | References | Coordinator | Collaborators
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2025-2)
CITES
Threat to humans
Human uses
More information
Food items (preys)
Diet composition
Food consumption
Food rations
Predators
Ecology
Growth parameters
Max. ages / sizes
Length-weight rel.
Length-length rel.
Length-frequencies
Mass conversion
Recruitment
Abundance
Reproduction
Maturity
Maturity/Gills rel.
Fecundity
Spawning
Spawning aggregations
Eggs
Egg development
Larvae
Larval dynamics
Gill area
Brain
Otolith
Body composition
Nutrients
Oxygen consumption
Swimming type
Swimming speed
Visual pigments
Fish sound
Diseases & Parasites
Toxicity (LC50s)
Genome
Genetics
Heterozygosity
Heritability
Genetic Diversity
Aquaculture systems
Aquaculture profiles
Strains
Ciguatera cases
Stamps, coins, misc.
Tools
Special reports
Download XML