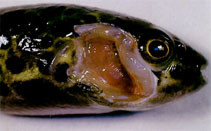
picture (DacGilD0.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |

picture (DacGilD1.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |
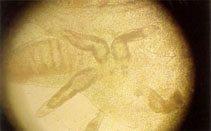
picture (DacGilD2.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |
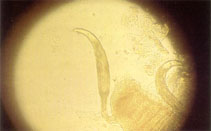
picture (DacGilD3.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |

picture (DacGilD4.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |

picture (DacGilD5.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |
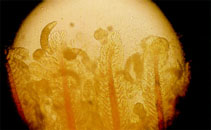
picture (DacGilD6.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |
picture (DacGilD7.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |
picture (DacGilD8.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |
picture (DacGilD9.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |
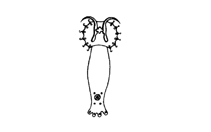
picture (DactylD0.gif) by Bassleer, G. |

picture (DactylD0.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |

picture (DactylD1.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |
picture (DactylD2.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |

picture (DactylD3.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |

picture (DactylD4.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |

picture (DactylD5.jpg) by Bassleer, G. |
cfm script by eagbayani, 10.05.99 ,
php script by kbanasihan 05/27/2010 ,
last modified by sortiz, 06.27.17